Minerals
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Service types
Scale
-
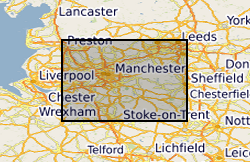
3200 mineral veins (i.e. lead, fluorspar) of the Southern Pennine Orefield within the Peak District National Park captured as a single dataset in 1983 from BGS 1:10 560 published maps with additional veins from referenced literature. The data covers a small, very limited area. Also includes several pipe and flat deposits. Also includes mapped faults. The dataset is approximately 99.5% complete. Uses for the data include economic geology, mineral resources, mine hazards. Veins are numbered but not named.
-

Rock and mineral samples (c.12 000) from former investigations of uranium resource potential in UK and overseas by the UK Atomic Energy Division and the Institute of Geological Sciences. Material samples are accompanied by paper registers, unpublished brief technical reports and a card index. Selected samples have been incorporated into the BGS Reference Mineral Collection (REFMINS) and hence recorded in the BRITROCKS database.
-
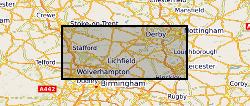
Zeta potential measurements of the fluorcarbonate mineral parisite-(Ce), under water, supernatant and collector conditions. Zeta potential measurements can be used to indicate the surface behaviour of a mineral under different reagent conditions. Mineral surface behaviour is important in processing and extracting minerals from their host ore, which can be energy intensive. Parisite-(Ce) is a fluorcarbonate mineral which contains rare earth elements. Rare earth elements are important in a wide range of products from iPhones to wind turbines.
-
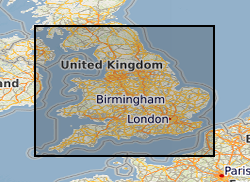
The full title of this project is" Studies into metal speciation and bioavailability to assist risk assessment and remediation of brownfield sites in urban areas" and is funded by NERC under the URGENT thematic programme form 1998-2001. The project is being undertaken by a consortium of workers from the Imperial College, University of Nottingham, and the British Geological Survey. Innovative collaborative and multi-disciplinary research will be applied to the interpretation of urban geochemical maps and associated meta-datasets to assist decision making by local authorities in the redevelopment of brownfield sites. Source apportionment, speciation and bioavailability of potentially toxic heavy metals will be studied at representative conurbations in the UK Midlands region. Scanning electron microscopy, chemical extractions and soil solution and vegetable analysis, will be integrated with high precision isotopic analyses of Pb and other potential toxic metals in this study. The results will be available as maps in GIS format to provide a generic decision support system for quantitative health risk assessment.
-

Thermochronological data from IODP Bengal Fan site 354. Grant abstract: The Himalayas are a type example of continent-continent collision, and resultant mountain building processes. Geologists can look at the rocks in the mountain belt itself to determine its evolution, but sometimes the evidence in the rocks in the mountain belt itself is obscured by later increases in the temperature and pressure that the rocks were subjected to, which overprints the evidence. Sediments eroded off the evolving Himalaya are deposited in the Bengal Fan, and these can provide an archive of the erosion of the history of the mountain belt through time which has not been obscured my later metamorphism, as the material was eroded and removed from the mountain belt prior to these later overprinting events. This project will analyse minerals that cooled as they were exhumed from deoth towards the surface in the mountain belt. The project will date the minerals to determine the time they cooled, and this will provide information on when the rocks were exhumed and how fast they exhumed, thus providing information on when and how fast the mountain belt grew.
-
The original version of this dataset contained lithologies interpreted as representing a mineral resource for mineral extraction. Collated on a County by County basis as part of the former Office of the Deputy Prime Minister (ODPM) Mineral Resource Information in support of National Regional and Local Planning between 1994 and 2006. A primary objective is to produce baseline data in a consistent format that can be updated, revised and customised to suit planning needs, including Mineral Local Plans and Regional Planning Guidance, as well as those of industry. The BGS Mineral Resource data does not determine mineral reserves and therefore does not denote potential areas of extraction. Only onshore, mainland mineral resources are included in the dataset. This dataset has been produced by the collation and interpretation of mineral resource data principally held by the British Geological Survey. The mineral resource data presented are based on the best available information, but are not comprehensive and their quality is variable. The dataset should only be used to show a broad distribution of those mineral resources which may be of current or potential economic interest. The data should not be used to determine individual planning applications or in taking decisions on the acquisition or use of a particular piece of land, although they may give useful background information which sets a specific proposal in context. During 2011-2012 revisions were made to areas of the resource linework. These changes were made as a result of new research and release of a new version of DiGMap (v5). This work was on an ad hoc basis but affects all resource layers. The paper maps were not re-released with this data update.
-
Collection of c.5,000 items relating to economic mineral exploration and exploitation in Scotland (with some records for Northern England) pre c.1960. Incorporates Non-Ferrous Metallic Ores Committee and Mineral Development Committee records. Collection originally arranged by mineral commodity, but new data is added in accession order.
-
Non-contact Atomic Force Microscopy images (NC-AFM) of surface nanobubbles on the carbonate mineral dolomite. Since surface nanobubbles were first imaged in 2000, they have been of growing interest to research due to their long lived properties, with reported lifetimes as long as several hours. Images of nanobubbles were produced under water, collector and depressant conditions using the air water supersaturation method. These are the first images of surface nanobubbles on dolomite. Surface nanobubbles could play a part in the processing of dolomite via froth flotation. These images lay a foundation for future analysis of the effect of nanobubbles in flotation.
-

Compiled by the Minerals Intelligence section of the Survey from 1918 to 1985. Comprises around 250,000 card entrys that refer to published articles on mineral topics world-wide.
-
This dataset comprises unprocessed microprobe analyses (WDS) of 10-15 natural zeolite samples, using the method of Campbell et al. (2016), and relating to the hypothesis of Campbell et al. (2012). Minerals analysed include stilbite, chabazite, phillipsite and harmotome. Key localities include the Western USA (oregon) and Europe (Germany and Scotland). Published papers and abstracts.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service