2019
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
Resolution
-
The data is presented as relative abundances of all species encountered in 300 counts on standard light microscope smear slides. Counts are presented from 64 samples, ranging from sample U1510A 48X 1W 50-51 cm (435.90 m) to U1510A 52X CC 24 cm (478.09 m). A second dataset provides semi-quantitative data from the same samples, which includes species that were not encountered during the 300 count.
-
This study explored the links between host rock composition, hydrothermal fluid composition (particularly pH), and the resulting ore minerals and deposits. The progressive water–rock reaction between 1 kg of initially acidic, condensed magmatic vapour and a series of different rock compositions was modelled with CHILLER (Reed, 1982, Reed, 1998), and follows the design of the water-rock reactions of Reed (1997). The thermodynamic data used in the numerical experiments are from the database SOLTHERM.H08 (Reed and Palandri, 2013). Data and calculations within SOLTHERM include: equilibrium constants calculated with SUPCRT92 (Johnson et al., 1992); mineral thermodynamic data for silicates, oxides, hydroxides, carbonates, gases (Holland and Powell, 1998) and sulphides (Shock, 2007). Mineral solid solutions are represented by end-member compositions that are mixed using an ideal multisite mixing scheme. Rock compositions used in the modelling represent a sub-alkaline andesitic control, and a number of alkaline compositions associated with world-class Au deposits. All starting rock compositions are derived from whole rock geochemical data, and have been recalculated to a 100% basis without TiO2 or P2O5 (excluded as minor phases with little to no effect on hydrothermal mineral assemblages). Original total Fe (as Fe2O3) has been recalculated to FeO and Fe2O3 using the method of Müller et al. (2001). The andesite is representative of calc-alkaline, silica saturated compositions, and is derived from and discussed in detail in Reed (1997). The Luise “Phonolite” (a trachyandesite using the Le Maitre et al., 1989 TAS plot; Fig. 1) and Trachyandesite are from the vicinity of the Ladolam epithermal Au deposit, Lihir Island, Papua New Guinea (Müller et al., 2001). The Porgera Mugearite and Feldspar Porphyry represent unaltered host rock compositions (Richards, 1990) from the Porgera Au deposit (Papua New Guinea). The Cripple Creek Phonolite is part of the host suite to the Cripple Creek epithermal Au deposit, Colorado (Kelley et al., 1998). The Savo trachyte (Smith et al., 2009) represents a typical host rock of the active hydrothermal system (Smith et al., 2010), on Savo island, Solomon Islands. With the exception of the Andesite, all compositions are alkaline using the total alkali versus silica definition of Irvine and Baragar (1971). The Savo sample is not associated with known epithermal Au mineralisation; this composition was selected on the grounds that it represents an evolved (SiO2-rich) silica-saturated, alkaline composition. The initial fluid composition is based on a condensate from Augustine volcano (Symonds et al., 1990) mixed 1:10 with pure water (Reed, 1997; Table 2). A single starting fluid for all models was chosen so as to demonstrate the effect of host rock alone.
-
Data files have .dat extension and can be opened with Notepad or any basic text editor software. Each file contains details of sample name, dimensions (length and diameter). All deformed samples were pre-prepared cylinders of synthetic neighbourite. Each file contains 11 data column as follows: Time (hours); Time (secs); CP (V); Vol (V); Force(V); Temp (V); Disp(V); Euro disp (mm); Furn T (mV); PoreP (mV); Furnace Power where V= Volts, mV= millivolts. The Calibration sheet (specific to the apparatus used) uploaded together with the data files is required to convert V and mV raw data into values of stress, strain, strain rate, confining pressure and temperature.
-
Whole-rock geochemistry data of samples collected from Tindfjallajökull volcano, south Iceland. For further information, see Moles, J. D. (2018). Volcanic archives of past glacial environments: Tindfjallajökull volcano, Iceland. PhD thesis, The Open University. http://oro.open.ac.uk/id/eprint/62117. Geographical extent: Bounding box latitude and longitude: SW corner 63°42'N 19°46'W and NE corner 63°50'N 19°28'W.
-
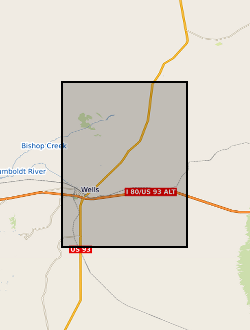
Ascii files or tables with earthquake source and model parameters determined for the Wells, Nevada earthquake
-
This data set contains 119 unwrapped and geocoded inteferograms derived from Cosmo-SkyMed (CSK) SAR scenes aquired over the Northen Main Ethiopian Rift between June 2014 and December 2015. This data set also contains displacement time series derived from processed CSK and Sentinel-1 inteferograms at the locations specified in the accompanying README files
-
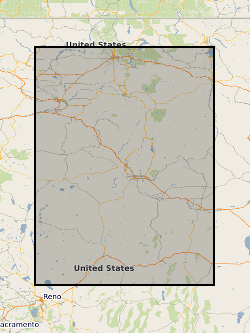
Processed SAR interferograms for the Wells, Nevada earthquake. Grant abstract: How do earthquakes happen? Understanding the nature of earthquakes is a key fundamental question in Geociences that holds many implications for society. Earthquakes are typically associated with a sudden release of energy that has slowly accumulated over hundreds to thousands of years, being strongly controlled by friction in faults buried several kilometers beneath our feet under quite extreme conditions. For example, the amount of heat produced in just a few seconds is such that it can dramatically change the nature of the fault zone near the sliding surface. Moreover, there is abundant evidence of substantial frictional weakening of faults (i.e., fault strength weakens with increasing slip or slip rate) during earthquakes. However, there are still many open questions related to earthquake source processes: How similar are earthquakes in different temperature-pressure conditions? What is the earthquake's energy budget, which controls the intensity of ground motions? What are the physical mechanisms responsible for fault weakening? Recent progress in seismological imaging methods, theoretical fracture mechanics and rupture dynamics simulations can help solve these questions. Huge volumes of freely available seismic and geodetic data from around the world now allow the routine calculation of earthquake models where earthquakes are typically described as single space-time points. Time is now ripe for systematically building robust, more detailed seismic models bearing information on earthquake's physics by using recently developed sophisticated modelling tools along with high-quality images of the 3-D Earth's interior structure enabled by high performance computing facilities. Moreover, it is now possible to model ruptures theoretically in detail using both analytical fracture mechanics calculations and numerical rupture dynamics simulations, and, for example, estimate the fault temperature during the rupture process, which is the most direct way to quantify friction. However, systematic quantitative links between these calculations and seismological observations are still lacking. This project addresses these issues through a coordinated effort involving seismology and rock mechanics aiming at estimating fault temperature rise during earthquakes from new macroscopic seismic source models. We will use advanced seismic source imaging methods to build a new set of robust kinematic, static and dynamic earthquake source parameters for a large selected set of global earthquakes (e.g., average fault length, width, rupture speed and time history, stress drop, radiated and fracture energy). These solutions will then be used as input parameters to estimate fault temperature using analytical and numerical rupture dynamics calculations. This will lead to an improved understanding of how local fault processes occurring at scales from few microns to tens of centimetres translate into macroscopic seismological properties, how energy is partitioned during earthquakes and which are the mechanisms responsible for fault weakening. Ultimately this project will shed new light on many basic questions in earthquake science such as the similarity of earthquakes in different P-T conditions and the potential geological record left by ruptures (e.g., melt). More broadly, this project will benefit hazard models and any studies relying on accurate earthquake source parameters such as studies in seismic tomography, active tectonics and microseismicity (e.g., associated with hydraulic fracturing).
-
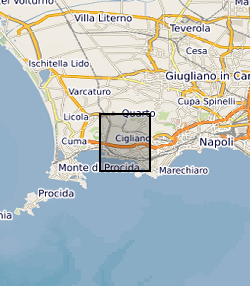
The data set contains location (latitude and longitude), ellipsoidal height (m) and observed gravity of benchmarks at the Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy. The gravity and location data were collected between 8 and 12 July, 2015 using a Scintrex CG5 gravimeter (serial number: 572) in tandem with a TOPCON HiPer Pro Dual-Frequency GNSS base and rover system. The survey contained a total of 85 benchmarks in addition to the base station.
-
(I) Handpump Vibration Data For each handpump, data is organized in one CSV file per day. These files are grouped together over batches, where each batch approximately corresponds to three months. (II) Borehole Water Level Data Water level data at the borehole of each handpump is recorded in one CSV file per handpump. Both uncompensated (raw) and compensated (with respect to atmospheric pressure) data are available. (III) Data Time Logs A separate Excel file lists the locations of the monitoring sites and the time logs corresponding to both (I) and (II) per handpump. References: [1] P. Thomson, R. Hope, and T. Foster, “GSM-enabled remote monitoring of rural handpumps: a proof-of-concept study,” Journal of Hydroinformatics, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 829–839, 05 2012. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2012.183 [2] F. Colchester, “Smart handpumps: a preliminary data analysis,” IET Conference Proceedings, pp. 7–7(1). [Online]. Available: https://digital-library.theiet.org/content/conferences/10.1049/cp.2014.0767 [3] H. Greeff, A. Manandhar, P. Thomson, R. Hope, and D. A. Clifton, “Distributed inference condition monitoring system for rural infrastructure in the developing world,” IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 19, no. 5, pp.1820–1828, March 2019. [4] F. E. Colchester, H. G. Marais, P. Thomson, R. Hope, and D. A. Clifton, “Accidental infrastructure for groundwater monitoring in africa,” Environmental Modelling Software, vol. 91, pp. 241 – 250, 2017. [Online]. Available:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364815216308325 [5] A. Manandhar, H. Greeff, P. Thomson, R. Hope, and D. A. Clifton, “Shallow Aquifer Monitoring Using Handpump Vibration Data,” In-review, 2019.
-
The RiftVolc GPS network was comprised of a total of 10 continuously recording stations deployed on Aluto and Corbetti Volcanoes between 2012 to present. At least 9 stations were recording data simultaneously except in 2012, 2016 and 2017 where 1, 8 and 5 stations were in operation respectively. Full details on station location and operation periods are provided in the attached README file.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service