2022
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
The BGS Debris Flow Susceptibility Model for Great Britain v6.1 is a 1:50 000 scale raster dataset of Great Britain providing 50 m ground resolution information on the potential of the ground, at a given location, to form a debris flow. It is based on a combination of geological, hydrogeological and geomorphological data inputs and is primarily concerned with potential ground stability related to natural (rather than man-made) geological conditions and slopes. The dataset is designed for those interested specifically in debris flow susceptibility at a regional or national planning scale such as those involved in construction or maintenance of infrastructure networks (road or rail or utilities), or other asset managers such as for property (including developers and home owners), loss adjusters, surveyors or local government. The dataset builds on research BGS has conducted over the past 15 years investigating debris flows. The model was designed to identify potential source-areas for debris flows rather than locate where material may be deposited following a long-run-out failure i.e. the track and flow of debris. This work focuses on natural geological and geomorphological controls that are likely to influence the initiation of debris flows. It therefore, does not consider the influence of land use or land cover factors.
-
Wind and surface morphological data collected at Medano Creek on the 15th April 2019 to investigate protodune initiation. Surface morphological data: This is terrestrial laser scanned (TLS) data collected of the creek sand surface using three different co-located Leica TLS (C10, P20 and P50). The data is raw point cloud format in text columns of x, y and z coordinate data. It has been orientation into the same local coordinate system. Each data set uses the same coordinate system. Data can be viewed in any spatial software. Data is labelled using C10, P20 or P50, followed by the scan number. Scan times are indicated in a seperate file. Wind data were collected from a fixed point next to the TLS instruments using a Gill 3D sonic anemometer. The data is in csv file format with column titles and can be viewed in any text or database software.
-
The data release includes surface and groundwater chemistry data from 86 samples (20 surface water, 60 ground water, and 6 ground water duplicates) collected during the baseline water monitoring at the UK Geoenergy Observatories (UKGEOS) Glasgow facility. This release from the British Geological Survey (BGS) covers surface and groundwater samples collected between 14 September 2020 and 20 May 2021 from 6 surface water sites, 5 mine water boreholes, and 5 environmental monitoring boreholes. The samples were then analysed for the concentrations of selected parameters at BGS and other laboratories. It contains a report and 2 data sheets GroundWaterChemData1 and SurfaceWaterChemData2. Version 2 06/09/2023 - Edits made to create consistency with subsequent data release, field included erroneously, removed.
-
Waterlines have been extracted to delimit the edge of the Hunga Tonga - Hunga Ha'apai island between April 2017 and April 2022. Waterline is defined as the instantaneous land - water boundary at the time of the imaging process. Waterlines have been generated by BGS - Earth Observation team through a thresholding-based classification based on Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery and developed on Google Earth Engine. Specifically, the thresholding has been applied to the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) has been derived as a basis to discriminate between the land and sea based on their spectral characteristics. Changes in waterlines over volcanic islands can provide key information to understand volcanic processes. For more info on the methodology, see Novellino et al. (2020) https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020536
-
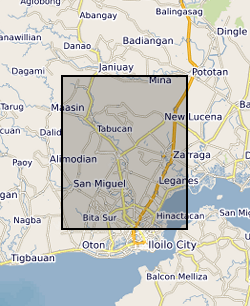
Ensemble of simulated groundwater levels for Iloilo, Philippines. The simulated time series of data covers the period December 1979 to December 2089 under two Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP2.6 and RCP 8.5). Each ensemble member csv file contains a timeseries of groundwater levels for thirteen locations within the Iloilo region. The textfile included in the folder shows the coordinates for these locations.
-

Seabed geology of the UK’s continental shelf, fine-scale maps providing detailed and accurate characterisation of the seabed geology, integrating substrate geology, structural geology and seabed geomorphology. Areas covered Anglesey, Bristol Channel, Dorset, East Anglia and Offshore Yorkshire. Mapping is based primarily on high-resolution bathymetry data produced by the UK Civil Hydrography Programme (CHP). Analysis and interpretation are further informed by secondary data and information resources, including; acoustic backscatter, physical samples (for example grabs, cores and boreholes), seismic data, academic and publicly accessible industry data and literature, and previous BGS mapping (onshore and offshore). The CHP is administered by the Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA), with technical oversight, data validation and onward charting undertaken by the UK Hydrographic Office (UKHO). The new fine-scale BGS Seabed Geology mapping comprise three complimentary components (or layers); substrate geology: distribution of bedrock and superficial geological units interpreted to be dominant within the top 1 m below seabed, structural geology: principal structural features such as faults and folds observed at rockhead and seabed geomorphology: physical morphology and interpreted geomorphic character of the seabed. These detailed geological digital maps are intended as enabling resources to better inform multiple offshore activities, research, and management of the marine environment. However, the seabed is a dynamic environment, where sediments may be in constant motion and sediment waves may migrate across the seafloor, burying or exposing the underlying hard substrate. Therefore, this data should not be relied on for local or site-specific geology. The mapping presented has been developed at a scale of 1:10 000 and should not be used at finer scales. Further detail on the mapping process and dataset characteristics are described within individual dataset user guides.
-
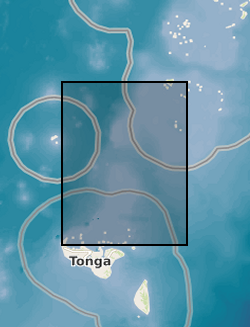
Tsunami trimlines identified across different islands of the Tonga archipelago. Trimlines have been used as a reference land feature following the January 2022 Tonga tsunami event that ripped off vegetation and built-up areas. Trimlines are distinctive limits between an area with sand coverage, vegetation destruction, and soil erosion on the one hand, and the unaffected natural vegetation on the other. This distinction provides a good landmark to map the inundation width and the landward extension of tsunami runup. In this case, the trimlines have been manually delineated by BGS - Earth Observation team using different high-resolution satellite datasets both optical (KompSat, Planet, Pleiades, WorldView) and radar (TerraSAR-X). Trimlines are well known from task-force publications documenting recent tsunami detection efforts and provide key information to support tsunami triggering mechanism models. For more info, see https://www.usgs.gov/media/images/tsunami-terms and Scheffers et al. (2012), https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9691-6
-
MicroCT (Micro–computed tomography) data of the left lower jaw of the Carboniferous stem tetrapod Crassigyrinus scoticus (GSE 4722), which was scanned in three parts (the specimen is preserved in three parts). The specimen was scanned at the Natural History Museum’s Imaging and Analysis Centre on a Nikon XH 225 microCT scanner in February 2013 and reconstructed as DICOM image stacks. All three parts were scanned at 210 kV and 240 mA. Part 1 represents the anterior part of the jaw and the scan produced 1995 transverse slices with a resolution of 0.1271 mm/voxel. Part 2 represents the middle part of the jaw and the scan produced 1995 transverse slices with a resolution of 0.1099 mm/voxel. Part 3 represents the posterior part of the jaw and the scan produced 1687 transverse slices with a resolution of 0.1099 mm/voxel. It was collected by Laura Porro and Jennifer Clack for anatomical description of the specimen and further biomechanical analyses.
-

We collect data from sensors located throughout the UK and beyond capturing information on properties such as groundwater temperature and levels, barometric air pressure and motion sensors. We have recently started collecting information related to the energy efficiency of buildings and have developed techniques for incorporating data from sensors operated by other institutions. Some of the data we collect is available through the sensor API and sensor dashboard which provides easy access to the API data.
-
Reflectance Transformation Imaging files of specimen BGS GSM106352, a large (1.0 x 1.2m) display cast, made from Jesmonite AC-300 and coloured dark gray and showing several species typical of the fossil biota on the Bed B surface of Wilby et al. (2011) in Charnwood Forest. Wilby. P, Carney, J.N, Howe, M.P.A 2011 A rich Ediacaran assemblage from eastern Avalonia: Evidence of early widespread diversity in the deep ocean. https://doi.org/10.1130/G31890.1
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service