Models
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
Elastic constants were calculated by using the stress-strain method and density functional theory for crystals of different symmetry. A toolkit was developed to facilitate the input preparation and output processing for elastic calculations using the Vienna Ab Initio Simulation Packge (VASP). The details of the calculation. methods, and the toolkit will be published elsewhere and linked to this deposit. The deposit contains example folders for the monoclinic, orthorhombic, trigonal, tetragonal, hexagonal and cubic lattices. The purpose of this deposit is to provide examples for the toolkit users.
-
Data for NERC grant NE/L000660/1. This is the data supporting Fig. 4 of the publication: Ebigbo, A., Lang, P. S., Paluszny, A., and Zimmerman, R. W. (2016). Inclusion-based effective medium models for the permeability of a 3D fractured rock mass. Transport In Porous Media, DOI: 10.1007/s11242-016-0685-z. It contains numerically computed permeabilities for various realisations of fracture networks. There are six different cases (as explained in the paper).
-
This dataset comprises ECLIPSE input decks for a 3D reservoir simulation of the CO2 plume at the Sleipner CO2 injection site. This whole reservoir model is an attempt to history match the growth of the plume observed on seismic data. A seismic velocity and density model derived from the 3D reservoir simulation is also included, together with a series of Seismic Unix scripts to create a synthetic seismic section through the Sleipner reservoir model, for comparison with released time-lapse seismic data.
-
ShapeCalc is an Excel-based tool that uses 2D crystal intersection widths and lengths to estimate 3D crystal shape. ShapeCalc provides 3D (S:I:L) shape estimates for 2D width-length (w-l) input data. Best estimates are found by comparing the sample w/l distribution with 2618 model w/l distributions covering shapes from 1:1:1 to 1:20:20. Model w/l distributions are obtained by 20000 random sections of a given model shape using the CSDCorrections algorithm (Higgins, 2000). For each model shape, the 20000 w/l datapoints are binned into 25 bins with w/l increments of 0.04. Binned distributions for all 2618 models are stored in the database tab. Compared to existing 2D-to-3D projection tools, ShapeCalc offers more robust constraints in 3D crystal shape (including uncertainty estimates) for a wider range of naturally occurring crystal shapes. ShapeCalc is described and published, with open access; Mangler, M.F., Humphreys, M.C.S., Wadsworth, F.B. et al. Variation of plagioclase shape with size in intermediate magmas: a window into incipient plagioclase crystallisation. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology 177, 64 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-022-01922-9
-
This data was collected as a part of the UK CCS Research Centre Call 2 Project C2-197: Multi scale characterisation of CO2 Storage in the United Kingdom. This is tabular data and X-ray imagery of drainage and imbibition relative permeability measured on reservoir rocks from the S. North Sea, N. North Sea, and E. Irish Sea of the Offshore UK. The data were obtained through measurements made at two distinct flow rates to allow for an evaluation of the impact of rock heterogeneity. Full details of the rock properties and experiments can be found in Reynolds et al. (2018) reference 3 below, the Final Report of the Project, as well as in the PhD Thesis of Catriona Reynolds with full references given below. Any use of the data should reference the journal article, reference 3 below. Geographical Area - Bunter sandstone in S. North Sea, Cleethorpes-1 Well, 1312.7-1316.1 m depth; Ormsirk sandstone in E. Irish Sea, Block 110/2a, 1247.9-1248.1 m depth; Captain sandstone in N. North Sea, Well 14/29a-3, 2997.6-3005.1 m depth. References 1. Imperial College London and British Geological Survey, Multiscale Characterisation of CO2 Storage in the United Kingdom, UKCCSRC Call 2 Project Final Report, 2016 2. Reynolds, C. Two-phase flow behaviour and relative permeability between CO2 and brine in sandstones at the pore and core scales, PhD Thesis, 2016, Imperial College London. 3. Reynolds, C.A., Blunt, M.J., Krevor, S. 2018, Multiphase flow characteristics of heterogeneous rocks from CO2 storage reservoirs in the United Kingdom, Water Resources Research, 54, 2, 729-745
-
General circulation model (HadCM3) output of the study by Matero et al. (2017) “The 8.2 ka cooling event caused by Laurentide ice saddle collapse. Data has been processed into netCDF4 - timeseries, and includes the following variables at model resolution: ocean temperature, ocean salinity, precipitation, air temperature at 2m height, depth of the oceanic mixed layer, sea ice concentration and meridional overturning circulation strength. The atmosphere component of the model has a horizontal resolution of 2.5° x 3.75° with 19 unevenly spaced vertical layers. The ocean component has a horizontal resolution of 1.25° x 1.25° with 20 unevenly spaced vertical layers. For more information see published paper, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.06.011
-
Dataset contains 3D synthetic seismic waveforms for axisymmetric global Earth velocity models. The waveforms were calculated using the finite difference approach with the PSVAxi algorithm (Jahnke, G et al., 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03744.x). The Earthmodels are 1D and use PREM parameters except close to the core-mantle boundary (CMB) where 3D ultra-low velocity zones (ULVZs) are added to the PREM background model. ULVZ are thin layers of strongly reduced seismic velocities located at the CMB that have been observed in several regions of the Earth. The dataset models interaction of the seismic wavefield with ULVZ structure with varying elastic parameters (P-wave, S-wave velocity, density), location (location at source or receiver side along the great circle path), ULVZ length, shape (box, Gaussian, trapezoid) and height. Detailed description of the approach and the model space are given in Vanacore et al, (2016). Data format is SAC (Seismic Analysis Code). Vanacore, E.A., Rost, S., Thorne, M.S., 2016. Ultralow-velocity zone geometries resolved by multidimensional waveform modelling. Geophys. J. Int. 206, 659–674. doi:10.1093/gji/ggw114
-
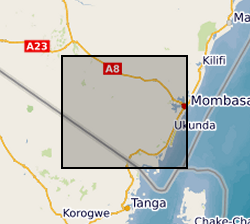
The download .rar file contains a groundwater model of the coastal aquifer in Kwale County, Kenya (ModelMuse Text File) produced by Dr Nuria Ferrer and Dr Albert Folch at the Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. The model can be used to explore future climate and groundwater abstraction scenarios to provide management recommendations. The download does not include proprietary abstraction data from industry project partners, thus running the model provided here will not reproduce published research findings. The file named”np67IH.bhd” are the initial heads file required to run the model.
-
Data output from the numerical flow modelling in GRL manuscript ""Evidence for the top-down control of lava domes on magma ascent dynamics"", by Marsden, L., Neuberg, J. & Thomas, M., all of University of Leeds. The models were created using the Laminar Flow module in COMSOL Multiphysics v5.4 by L. Marsden. The following files are uploaded: Archive_Reference_Model.txt (Reference flow model: Gas loss function, Initial H2O content = 4.5 wt.% Excess pressure at depth = 10 MPa, Constant corresponding to crystal growth rate = 4e-6 s^-1 ) Archive_High_H2O.txt (Gas loss function, Initial H2O content = 10 wt.% Excess pressure at depth = 10 MPa, Constant corresponding to crystal growth rate = 4e-6 s^-1) Archive_No_Gas_Loss.txt (No gas loss, Initial H2O content = 4.5 wt.% Excess pressure at depth = 10 MPa, Constant corresponding to crystal growth rate = 4e-6 s^-1) Archive_Gamma_Low.txt (Gas loss function, Initial H2O content = 4.5 wt.% Excess pressure at depth = 10 MPa, Constant corresponding to crystal growth rate = 1e-6 s^-1) Archive_Excess_Pressure_0MPa.txt (Gas loss function, Initial H2O content = 4.5 wt.% Excess pressure at depth = 0 MPa, Constant corresponding to crystal growth rate = 4e-6 s^-1) Archive_Excess_Pressure_20MPa.txt (Gas loss function, Initial H2O content = 4.5 wt.% Excess pressure at depth = 20 MPa, Constant corresponding to crystal growth rate = 4e-6 s^-1) The files uploaded include the reference flow model and where a single key parameter has been changed in the flow modelling. We include data where the key parameter is at the upper or lower limit of the values tested. Data are not included where magma ascent is modelled to stall without the extrusion of a lava dome, as a time dependent model is not run in this case. A solution is provided using equilibrium modelling only. The following variables are output, at conduit centre unless specified: Depth (m), Time(s), Ascent velocity (m/s), Bulk Viscosity (Pa s), Crystal Content, Dome height (m), Gas Volume Fraction, Overpressure (Pa), Shear Stress at Conduit Wall (Pa)
-
UKCCSRC Call 2 Project C2-197 - The dataset comprises a series of ECLIPSE 100 input decks describing reservoir models of potential CO2 storage sites in the Southern North Sea and East Irish Sea offshore UK. The models were developed to test the effect of relative permeability hysteresis on the geological storage of CO2. The models incorporate new relative permeability datasets measured by Imperial College, London as part of the CO2MULTISCALE project.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service