Coal fields
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
-

**has been incorporated into the main BGS Landslides database**The dataset results from a survey of the landslips in the South Wales Coalfield, conducted on contract for the Department of the Environment in 1977-81. A total of 579 landslips were identified from air photo interpretation and existing mapping. Each landslip was examined in the field and a catalogue compiled including data on location, description, classification, geological context, dimensions and activity. The data is also presented on c. 90 annotated field sheets at 1:10 000 scale and in other supporting documentation.
-

These images were acquired using micro computed tomographic imaging of 4 sandstone plugs taken at various depths in the Glasgow UKGEOS borehole GGC01. GG496 (170.07 m), GG497 (168.66 m), GG498 (73.37 m) and GG499 (135.06 m). These samples are further detailed and analysed in the following article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1144/petgeo2020-092.
-

Reports detailing investigations into mine water discharges and potential effects on aquifers in the East Midlands Coalfield and in the Lake District.
-
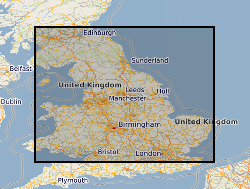
This dataset provides the first map and synthesis of the temperature of Britain's coalfields. It was created to support low-temperature heat recovery, cooling and storage schemes using mine water in abandoned workings. This baseline spatial mapping and synthesis of coalfield temperatures offers significant benefit to those planning, designing and regulating heat recovery and storage in Britain's abandoned coalfields. The dataset has been developed jointly by the Coal Authority and the British Geological Survey. It is delivered as a hexgrid representing mine water blocks, identifying equilibrium mine temperatures at 10 depth intervals (100 m > 1000 m) and pumped mine temperatures at 6 depth intervals (100 m > 600 m).
-
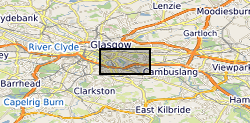
The UK Geoenergy Observatories (UKGEOS) Glasgow bedrock model outputs, created by the British Geological Survey, provide a semi-regional overview of the depth and extent of bedrock lithostratigraphic units, coals and faults. The model allows users to visualise the likely subsurface sequence to be found beneath this part of Glasgow, applicable at a scale of around 1: 25,000 to 1: 10,000. The data is supplied as grids, triangulated surfaces and shapefiles over a 5 by 4.15 km area, with the depth range to around 350 m below Ordnance Datum. This model describes an interpretation of the bedrock geology before the UKGEOS Glasgow boreholes have been drilled, and was used to inform the expected sequence on drilling. Further details and model limitations can be found in the accompanying metadata report http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/522737.
-
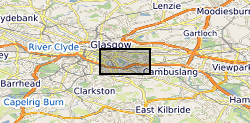
The UK Geoenergy Observatories (UKGEOS) Glasgow 3D coal mine model outputs, created by the British Geological Survey, provide a semi-regional overview of the depth and extent of surveyed and probable coal mine workings, plus stone and coal roads surveyed within the mines. The model allows users to visualise the surveyed and probable coal mine workings to be found beneath this part of Glasgow, applicable at a scale of around 1: 25,000 to 1: 10,000. The data is supplied as grids, triangulated surfaces over a 5 by 4.15 km area, with the depth range to around 300 m below Ordnance Datum. The mine extents are ‘cut out’ of the UKGEOS Glasgow post-drill bedrock model. This model describes both surveyed (recorded on mine abandonment plan) and probable coal mine workings. An area of probable workings has been updated to account for the results of drilling borehole GGC01. Further details and model limitations can be found in the accompanying metadata report http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/531157/
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service