Image (GeoTIFF)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
Resolution
-

The UK Compiled Topsoil Dataset (UKTS) is the most extensive topsoil geochemistry dataset for the UK available at the time of release (August 2024). The dataset consists of 82 georeferenced TIFF raster images (GeoTIFF format) with a cell size of 500 x 500 m, displaying the predicted concentrations for 41 chemical elements in UK topsoil and their respective standard error. The dataset is based on the geochemical analyses of 57,966 topsoil samples collected between 1978 and 2014 and analysed by X-Ray Fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The UKTS was brought together by combining data from the following sources: i. the British Geological Survey’s (BGS) Geochemical Baseline Survey of the Environment (G-BASE) rural and urban topsoil dataset (which accounts for 76.4% of the topsoil samples included in the UKTS) ii. the Geological Survey of Northern Ireland (GSNI) TellusNI rural and urban topsoil geochemical survey dataset (13.8% of the UKTS samples) iii. the BGS-Rothamsted Research X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (XRF) rural soil dataset (RR-BGS XRF), based on sub-samples held at Rothamsted Research from the National Soil Inventory (NSI) of England and Wales sample archive, National Soil Resources Institute, Cranfield University (9.8% of the UKTS samples). An atlas of the compiled topsoil concentrations for the UK is available to download (https://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/535963) and all maps are available to view within the UK Soil Observatory website (https://www.ukso.org). The dataset covers England, Wales and Northern Ireland, and the Clyde Basin in Scotland. The GeoTIFF raster image maps were produced from the interpolation by ordinary kriging of the concentration values in the source data points, using the geostatistical wizard in the geostatistical analyst toolbox of ESRI ArcGIS 10.8.
-
The BGS Geochemical Baseline Survey of the Environment (G-BASE) was the national strategic geochemical mapping programme in Great Britain. The project set out to establish the chemistry of the surface environment by the collection and analysis of stream sediment, stream water and soil samples. Beginning in the late 1960s in northern Scotland and moving southwards across the country, the primary focus was mineral exploration, however, the project quickly developed to address important environmental concerns. The final G-BASE samples were collected in southern England in 2014. The outputs from the G-BASE project provide an invaluable, systematic baseline of geochemical information for Great Britain, serving as a marker of the state of the environment against which to measure future change. Deep soil samples (also known as profile soil samples) were taken from depths of between 35 cm and 50 cm at densities of 1 sample per two square kilometres (rural / regional areas) and 4 samples per square kilometre (urban areas). The G-BASE profile soils were generally sieved to 150 microns before analysis and determined by XRF for some or all of: Ag, As, Ba, Bi, Br, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Fe, Ga, Ge, Hf, I, K, La, Mg, Mn, Mo, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, Rb, Sb, Sc, Se, Se, Sn, Sr, Ta, Te, Th, Ti, Tl, U, V, W, Y, Zn and Zr. Since 2003, for both regional and urban sampling, deep soil samples and shallow soil samples were routinely collected from the same sites, but only the shallow soil samples were submitted for chemical analysis. The deep soil samples were archived in the National Geoscience Data Centre. For more information about accessing these samples and their analytical results, contact BGS Enquiries (enquries@bgs.ac.uk).
-
The British Geological Survey (BGS) holds an archive of multibeam backscatter data from BGS, the Maritime & Coastguard Agency (MCA) and other organisations. The data are stored within the National Geoscience Data Centre (NGDC) as the Marine Environmental Data and Information Network (MEDIN) Data Archive Centre (DAC) for geology and geophysics. The majority of the data were collected and processed for the Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA) under the Civil Hydrography Programme (CHP). Backscatter image files for a survey can be downloaded (in GeoTIFF format) using the URL link provided or via the Deposited Data Search (https://webapps.bgs.ac.uk/services/ngdc/accessions/index.html?simpleText=backscatter&subjectList=3159). Backscatter data are useful for seabed characterisation for geological and habitat mapping. BGS works with the DAC for bathymetry data at the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO) to archive the backscatter data. View and download the related bathymetry data via the ADMIRALTY Marine Data Portal: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/inspire-portal-and-medin-bathymetry-data-archive-centre.
-
This dataset comprises two collections of maps. The facsmile collection contains all the marginalia information from the original map as well as the map itself, while the georectified collection contains just the map with an associated index for locating them. Each collection comprises approximately 101 000 monochrome images at 6-inch (1:10560) scale. Each image is supplied in TIFF format with appropriate ArcView and MapInfo world files, and shows the topography for all areas of England, Wales and Scotland as either quarter or, in some cases, full sheets. The images will cover the approximate epochs 1880's, 1900's, 1910's, 1920's and 1930's, but note that coverage is not countrywide for each epoch. The data was purchased by BGS from Sitescope, who obtained it from three sources - Royal Geographical Society, Trinity College Dublin and the Ordnance Survey. The data is for internal use by BGS staff on projects, and is available via a customised application created for the network GDI enabling users to search for and load the maps of their choice. The dataset will have many uses across all the geoscientific disciplines across which BGS operates, and should be viewed as a valuable addition to the BGS archive. There has been a considerable amount of work done during 2005, 2006 and 2007 to improve the accuracy of the OS Historic Map Collection. All maps should now be located to +- 50m or better. This is the best that can be achieved cost effectively. There are a number of reasons why the maps are inaccurate. Firstly, the original maps are paper and many are over 100 years old. They have not been stored in perfect condition. The paper has become distorted to varying degrees over time. The maps were therefore not accurate before scanning. Secondly, different generations of maps will have used different surveying methods and different spatial referencing systems. The same geographical object will not necessarily be in the same spatial location on subsequent editions. Thirdly, we are discussing maps, not plans. There will be cartographic generalisations which will affect the spatial representation and location of geographic objects. Finally, the georectification was not done in BGS but by the company from whom we purchased the maps. The company no longer exists. We do not know the methodology used for georectification.
-

The dataset portrays heat flow as a continuous modelled surface, interpolated between observation points. Onshore coverage is provided for England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. The British Geological Survey (BGS) Heat flow dataset version 1 (United Kingdom) is derived from a catalogue of legacy heat flow observations and ground-heat modelling. Heat flow data is typically used to determine temperatures beneath the ground surface, and model how much thermal energy may be stored in or recovered from the ground. The dataset is presented as a raster model, but is also available as cellular, vector grids. The raster and square-cellular grid defines each cell by an area of c. 4km2 (2km per side). The hexagonal-cellular defines each cell by an area of c. 2.56km2 (1km per side). Heat flow values are milli-Watts per square metre (mWm-2). The data are available under BGS data licence. For more information, see the user guide: https://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/539413 (BGS Open Report OR/25/013).
-
The HiRES-1 project acquired airborne geophysical data during 1998. Coverage included the Central Midlands of England and into the associated Welsh Borderland. Survey flying for the collaborative BGS and World Geoscience Corporation Ltd (WGC) high resolution geophysical and environmental survey was completed in early September 1998. The data comprise multi-channel gamma ray spectrometer, magnetometer and dual frequency VLF-EM. Flight line spacing was 400 m with tie lines at 1200 m and the total area surveyed is some 14 000 km2. Flight-line orientations are W–E over the western survey area, SW–NE over the eastern area. Ground clearance was maintained at 90 m in rural areas, increasing to about 240 m in built-up zones. The project and data descriptions are provided in an internal BGS report: R J Peart, R J Cuss, D Beamish and D G Jones, 2003. The High Resolution Airborne Resource and Environmental Survey- Phase 1 (HiRES-1): background, data processing and dissemination and future prospects. British Geological Survey Internal Report, IR/03/112. 28pp.
-
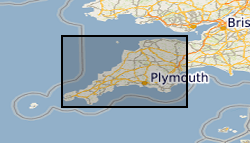
Airborne geophysical data acquired as part of the BGS-NERC TellusSW project (http://www.tellusgb.ac.uk/) during the second half of 2013. The survey comprised a high resolution magnetic/magnetic gradient survey combined with a multichannel (256 channel) radiometric survey. The survey was carried out using 200m (N-S) line separations at a mean elevation of 91m. Encompassing the counties of Cornwall and parts of Devon and Somerset, the survey provided 60,323 line-km of data. Digital data and derived (e.g. spatial derivatives) maps of the geophysical information are provided to facilitate spatial modelling of the soil, geological and environmental aspects of the data.
-

CO2 was injected into shallow unconsolidated marine sediments in Ardmucknish Bay, Oban. 2D seismic reflection data were collected pre-release (15/05/2012), syn-release (17/05/2012, 18/05/2012, 19/052012, 29/05/2012, 30/05/2012, 20/06/2012) and after release stages (23/04/2014 and 24/04/2014) of CO2 help to better understand the spatial and temporal evolution of free gas anomalies within the overburden. The impact of CO2 on sediment acoustic properties, namely seismic reflectivity and attenuation, was also investigated. This dataset was collected by the National Oceanography Centre Southampton (NOCS) and the British Geological Survey (BGS) under the program QICS (Quantifying and monitoring environmental impacts of geological carbon storage) which was funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), with support from the Scottish Government. The dataset includes segy files, a presentation which summarises the main results and a map showing the spatial extent of the seismic data collected after gas release. QICS project website: http://www.bgs.ac.uk/qics/home.html. Cevatoglu et al., 2015. Gas migration pathways, controlling mechanisms and changes in sediment acoustic properties observed in a controlled sub-seabed CO2 release experiment. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control. DOI:10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.03.005. The post-release data is currently restricted. NERC grant NE/H013873/1
-

This dataset contains data from a marine geophysical and multibeam survey which took place in April 2012 in the area of Ardmucknish Bay on board the RV White Ribbon. This was a follow up survey to the previous work carried out in this area in 2011 (2011/4). QICS (Quantifying and monitoring potential ecosystem impacts of geological carbon storage) was a scientific research project funded by NERC; its purpose was to improve the understanding of the sensitivities of the UK marine environment to a potential leak from a carbon capture storage (CCS) system. The aim of the survey was to assess any affect the drilling of the borehole had on the underlying sediments. Sea floor bathymetry data were collected using a Kongsberg EM3002D multibeam system. Sub bottom seismic profiling data were collected using an Applied Acoustics surface tow boomer (STB). Technical details of the survey are contained in the BGS Report of Survey. Webpage www.bgs.ac.uk/QICS/. NERC Grant NE/H013954/1.
-

This dataset contains data from a marine multibeam and geophysical survey which took place in June 2011 in the Ardmucknish Bay area on board the BGS survey vessel RV White Ribbon. The survey was carried out by the British Geological Survey (BGS) in collaboration with Scottish Association for Marine Science (SAMS) and National Oceanography Centre (SAMS). QICS (Quantifying and monitoring potential ecosystem impacts of geological carbon storage) was a scientific research project funded by NERC. The purpose was to collect the data necessary to identify a potential directional drilling route from shore to a submerged gas release point. Sea floor bathymetry data were collected using an EM3002D. Sub bottom seismic profiling data were collected using a surface tow boomer. Technical details of the survey are contained in the BGS Report of Survey. Webpage www.bgs.ac.uk/QICS/. NERC Grant. NE/H013962/1.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service