Shale
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
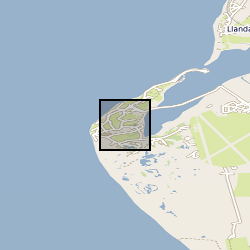
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) scans of four samples of consolidated shale from the Lower Jurassic (C.exaratum subzone) of the Cardigan Bay Basin (Wales, UK). The samples were taken from the Mochras Core, at depths of 789, 810, 812, and 818m (all samples within data measured in metres). Each sample is distinguished by its unique sample identification number (SSK). For each sample, there is a stack of XCT orthoslices (.tiff) files, and for SSK109633, an incomplete Avizo file. Mochras core location (aprox.) 52°48'39.74"N, 4° 8'48.09"W. Mochras Island, west of Llanbedr, Gwynedd, Wales, UK
-
The mechanical data (confining and injection pressures) recorded during Vickers indentation experiments on samples of shale materials. These experiments were conducted on the I12 beamline, Diamond Light Source, Harwell as part of beamtime EE17606-1 between 31/01/18 and 05/02/18.
-
The mechanical data (loads, displacements) recorded during double torsion experiments on samples of 6 shale materials and a sandstone. These experiments were conducted on the I12 beamline, Diamond Light Source, Harwell as part of beamtimes EE13824-1 and EE13824-2 between 26/02/17 and 03/03/17. The data were collected using the standard double-torsion technique, with a load cell behind the actuator recording applied force. The method and results are described in detail by Chandler et al, (2018,submitted) "Correlative optical and X-ray imaging of strain evolution during Double Torsion Fracture Toughness measurements in shale" The data was collected with the aim of correlating local deformation around a progressing fracture (through X-Ray and optical imaging) with recorded mechanical data from the loading system. The data was collected by M. Chandler, A-L Fauchille, J. Mecklenburgh, H. K. Kim and L. Ma, and was processed by M. Chandler and R. Rizzo. The complete dataset is present.
-

These data accompany a manuscript, titled: Stream and Slope Weathering Effects on Organic-rich Mudstone Geochemistry and Implications for Hydrocarbon Source Rock Assessment: A Bowland Shale Case Study All files with prefix 'Man_1' relate to this submission. The manuscript was submitted to the journal Chemical Geology in December 2016. Data include: 1) A range of photographs from the outcrop, drill cores, sub-samples, 'weathering grades' and thin section microphotographs from the Bowland Shale; 2) The results of mineralogical (whole rock powder x-ray diffraction; XRD) analyses for 18 subsamples; 3) The results of inorganic geochemical analyses (LECO elemental C and S, x-ray fluorescence major and trace elements) for 18 subsamples; 4) The results of organic geochemical analyses (Rock-Eval pyrolysis, d13Corg) for 20 subsamples; 5) RStudio scripts used to conduct statistical analyses (e.g., Principal Components Analysis) and generation of figures.
-

These data comprise geochemical results from upper Ediacaran organic-rich shales / mudstones from the Yangtze Craton (South China) from the Doushantuo Formation (member IV) and overlying lower Dengying Formation (= Miaohe Member). Ages range from about 570 to 550 Ma. The data consist of iron partitioning (Fe-speciation), phosphorus partitioning (P-speciation), bulk rock metal concentrations, total organic content and pyrite sulfur isotopes. Major and trace element concentrations of all samples were measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry and mass spectrometry, respectively, after quantitative HNO3-HFHClO4 digestion. Fe speciation was performed after the established methodology of Poulton and Canfield to extract operationally defined Fe phases, including Fe associated with carbonates (Fecarb), ferric oxides (Feox), magnetite (Femag), and pyrite (Fepy). The sum of these Fe pools constitutes the proportion of Fe that is considered highly reactive (FeHR) toward dissolved sulfide. Ratios of FeHR/FeT > 0.38 support FeHR enrichment and deposition under anoxic bottom water conditions, whereas values of <0.22 indicate deposition from oxic bottom waters. The intermediate range of 0.22 to 0.38 is regarded as equivocal because of the possibility for rapid sediment deposition or early diagenetic transformation of unsulfidized FeHR to poorly reactive sheet silicate minerals. For anoxic samples (FeHR/FeT > 0.38), the degree of sulfidation of the FeHR pool can be used to distinguish ferruginous (Fepy/FeHR <0.7) from euxinic (Fepy/FeHR > 0.8) conditions, with an intermediate zone ascribed to “possible euxinia”. Recent analyses of Holocene sapropels and the euxinic Lake Cadagno indicate that Fepy/FeHR > 0.6 may be a more suitable threshold for distinguishing ferruginous from possible euxinic conditions. Selected shale samples were analyzed for pyrite sulfur isotopes (δ34Spy), TOC, organic carbon isotopes (δ13Corg), and P phase associations. The P measurements use a sequential extraction method to distinguish the proportion of total P (PTot) associated with detrital apatite (Pdet) relative to potentially bioavailable and reactive (Preac) minerals, including Fe (oxyhydr)oxides (PFe),organic matter (Porg), and authigenic carbonate fluorapatite, biogenic apatite, and CaCO3-bound P (Pauth). For methods, see: S. W. Poulton, D. E. Canfield, Development of a sequential extraction procedure for iron: Implications for iron partitioning in continentally derived particulates. Chem. Geol. 214, 209–221 (2005). Fred T. Bowyer, Alexander J. Krause, Yafang Song, Kang-Jun Huang, Yong Fu, Bing Shen, Jin Li, Xiang-Kun Zhu, Michael A. Kipp, Lennart M. van Maldegem, Jochen J. Brocks, Graham A. Shields, Guillaume Le Hir, Benjamin J. W. Mills, and Simon W. Poulton Biological diversification linked to environmental stabilization following the Sturtian Snowball glaciation. Sci. Adv. 9 (34), eadf9999. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adf9999 (2023)
-
The dataset describes the results of high pressure experimental measurements of three contrasting 'tight' rocks; a Bowland Shale, a Haynesville shale and Pennant sandstone. The results are tabulated as a csv file, listing experimental parameters, confining pressure, argon gas pore pressure and permeability. complementary measurements of key petrophysical data are provided - bulk modulus of compressibility, porosity TOC and density.
-
This data set contains seismic source parameters (magnitudes, corner frequencies, stress drops and their associated uncertainty) for 94 microseismic events linked to fault reactivation during hydro-fracturing operations in the Horn River Basin (British Columbia). The data presented here were derived from proprietary third party seismic data recorded on 2 arrays of 35 - 15 Hz GEO-OMNI-2400 borehole geophones each. These data were first reported in Adam G Klinger, Maximilian J Werner, Stress drops of hydraulic fracturing induced microseismicity in the Horn River basin: challenges at high frequencies recorded by borehole geophones, Geophysical Journal International, Volume 228, Issue 3, March 2022, Pages 2018–2037, https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggab458
-

Loan IDA number - IDA271576. No data was obtained for microbial cultivation experiments with core samples SSK111460 and SSK111461 from UKGEOS Glasgow Observatory, borehole GGC01. Samples and data are derived from the UK Geoenergy Observatories Programme funded by the UKRI Natural Environment Research Council and delivered by the British Geological Survey. Attached document described methodology of enriching sandstone core (SSK111461) in different media types and shale core (SSK111460) in synthetic groundwater. No microbial growth was seen after 7 months.
-
A worldwide compilation of 645 analyses of Sm and Nd concentrations, and Nd isotopes, in fine-grained continental sedimentary rocks with a range of deposition ages. These data were used in Dhuime et al. (2017, Sedimentary Geology 357, 16-32) to calculate the variation in the Nd model age of fine-grained continental sediments as a function of their age of deposition.
-
Whole rock and sediment geochemical data covering a range of elements, where values are given in ppm (parts per million) or as a % (percentage). The data is ordered chronologically in an excel spreadsheet and each sample is given a ‘Sample ID’, ‘Lithology’, ‘Locality’, ‘Age’ and ‘Date analysed’, followed by whole rock and sediment values for the following elements; Ag, Al, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Bi, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Fe, Ga, Ge, Hf, Hg, In, K, La, Li, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Nb, Ni, P, Pb, Pd, Pt, Rb, Re, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Sn, Sr, Ta, Te, Th, Ti, TI, U, V, W, Y, Zn, Zr. Cells which are highlighted orange signify that the value given was below the detection limit. The values in orange cells have been halved to maintain spreadsheet functionality (i.e. to remove ‘<’ symbols). Cells which have been highlighted blue signify that the value given was above the detection limit. ALS method:ME-MS41L (https://www.alsglobal.com/en/services-and-products/geochemistry/geochemistry-testing-and-analysis/whole-rock-analysis-and-lithogeochemistry) . The majority of the samples included in this data were collected in the UK, but, where appropriate, samples out with the UK were included. The majority of the data was collected from 2014 to 2019. Whole rock and sediment samples were analysed by solution ICP-MS. Samples of ~30 g were individually milled and homogenised, and 0.5 g were digested with aqua regia in a graphite heating block. The residue was diluted with deionised water (18 M¿ cm), mixed, and analysed using a Varian 725 instrument at ALS Minerals (Loughrea; method ID: ME-MS41L). This data was collected to better understand the low temperature cycling of Telurium (Te) and Sellenium (Se) in the geological environment. For example, a range of ochre samples were included in this database. Ochres are a modern precipitate commonly found in rivers and streams which flow through geographical areas with a history of mining resources which are rich in sulphides. Iron from the sulphides are leached out and deposited downstream, coating river and stream beds, giving a red, yellow or orange colouration. Ochres can be a sink for trace metals, so analysing the abundances of these can be informative from a resource perspective but also from an environmental hazard perspective. This would be useful for researchers who require reference data for whole rock and sediment data of a particular lithology or age. This data is was collected by, but not limited to the following individuals; John Parnell, Sam Spinks, Josef Armstrong, Liam A Bullock, Magali Perez, Xueying Wang & Connor Brolly.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service