Monsoon
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
This is a point (.txt) file of 12,838 Asia Summer Monsoon (ASM) - triggered landslides that occurred across central-eastern Nepal in the period 1988 - 2018. This inventory includes the landslide locations (x, y coordinates of landslide crests) and geometries, as well as the following landslide attributes, where each attribute was extracted at the position of the landslide crest: elevation (m), slope (o), aspect (o), planform and profile curvature, excess topography (m3), local relief (m), distance to channel (m), distance to road (m), near channel ksn, near channel specific stream power (SSP), average 30-year precipitation, total annual rainfall, peak monthly rainfall, landuse, Permafrost index, geology, and tectonic unit. Note, landslides were not mapped in the years 2011 and 2012 due to scan line errors in the Landsat 7 imagery. These landslides and associated attributes were collected for the purpose of assessing how landslide spatial distributions and susceptibility vary through time.
-
This is a polygon Shapefile of 12,920 Asia Summer Monsoon (ASM) - triggered landslides that occurred across central-eastern Nepal in the period 1988 - 2018. This inventory includes the landslide locations, perimeters (Length field), areas and pre-/post- monsoon season satellite image dates used to map each landslide.Note, landslides were not mapped in the years 2011 and 2012 due to scan line errors in Landsat 7 imagery. These landslides were mapped for a range of purposes, from conducting landslide susceptibility assessments, to investigating landslide processes and preconditioning.
-
This is a polygon Shapefile of 12,838 Asia Summer Monsoon (ASM) - triggered landslides that occurred across a ~45,000 km2 region of central-eastern Nepal in the period 1988 - 2018. This inventory includes the landslide locations, perimeters (Length field), areas and pre-/post- monsoon season satellite image dates used to map each landslide. Note, landslides were not mapped in the years 2011 and 2012 due to scan line errors in Landsat 7 imagery. These landslides were mapped for a range of purposes, from conducting landslide susceptibility assessments, to investigating landslide processes and preconditioning.
-
Simulations made using the HadGEM2 model in AMIP (atmosphere only) configuration for the SAPRISE (South Asian PRecIpitation: A SEamless assessment) project. The SAPRISE project investigates the impacts of aerosols on the South Asian Monsoon using historical simulations forced with anthropogenic aerosols i.e. sulphur dioxide, black carbon and biomass burning aerosols. The simulations cover the period from 1850-2000.
-
Groundwater level measurements collected by the state groundwater boards of Punjab and Haryana states, India, and by the Central Groundwater Board. The data consist of well locations and measurements of groundwater levels, in metres below the top of the well casing. Data were collected in both the pre-monsoon (May-June) and post-monsoon (October-November) periods. Data availability is irregular across the entire suite of wells.
-
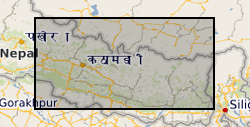
This file contains the point data and areas (in m) of 12,838 monsoon-triggered landslides that occurred during distinct monsoon seasons between 1988 and 2018 across a 45,000 km2 region of central-eastern Nepal.
-
Benthic stable isotope (carbon and oxygen) data from IODP Site U1445. Generated by Yasmin Bokhari-Friberg, supervisied by Kate Littler and Pallavi Anand.
-
This dataset contains raw beaching data computed by marine debris simulations (run using OceanParcels) for a range of physical scenarios (surface currents from GLORYS12V1 (https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.698876), Stokes drift from WAVERYS (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-020-01433-w), and surface winds from ERA5 (https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3803)), as described in the accompanying manuscript. Through postprocessing, debris ‘connectivity’ matrices can be computed, providing predictions for the main terrestrial and marine source regions of plastic debris accumulating at remote islands in the western Indian Ocean. These simulations include beaching and sinking processes, and a set of example matrices is provided here (https://doi.org/10.5287/bodleian:DEdqwXZQw). However, these matrices can be recomputed for different sinking and beaching rates using the scripts archived here (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7351695), or see here (https://github.com/nvogtvincent/WIO_Marine_Debris/) for the live version with documentation. These predictions will be useful for environmental practitioners in the western Indian Ocean to assess source regions for marine debris accumulating at islands of interest, and when this debris is likely to beach. The data were produced as part of the Marine Dispersal and Retention in the Western Indian Ocean project funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) grant NE/S007474/1. See linked online references on this record for cited items given above.
-
An ensemble of simulations made using the Unified Model version 6.6 (HadGEM2) in AMIP (atmosphere only) configuration for the SAPRISE (South Asian PRecIpitation: A SEamless assessment) project. The simulations are used to investigate the impacts of aerosols on the South Asian Monsoon. The four-member ensemble of simulations are forced with anthropogenic-only aerosols i.e. sulphur dioxide, black carbon and biomass burning aerosols. The simulations cover the period from 1850-2000. Since aerosol-only simulation is not compulsory in CMIP5, these four runs are complements to other CMIP5 simulations conducted by Met Office using the HadGEM2-ES (vn 6.6).
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service