Jurassic
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
-
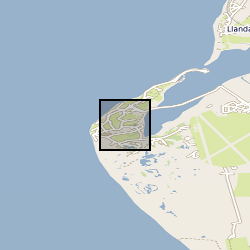
X-ray computed tomography (XCT) scans of four samples of consolidated shale from the Lower Jurassic (C.exaratum subzone) of the Cardigan Bay Basin (Wales, UK). The samples were taken from the Mochras Core, at depths of 789, 810, 812, and 818m (all samples within data measured in metres). Each sample is distinguished by its unique sample identification number (SSK). For each sample, there is a stack of XCT orthoslices (.tiff) files, and for SSK109633, an incomplete Avizo file. Mochras core location (aprox.) 52°48'39.74"N, 4° 8'48.09"W. Mochras Island, west of Llanbedr, Gwynedd, Wales, UK
-
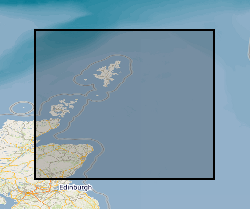
This dataset shows the distribution of Middle Jurassic, Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous lithostratigraphic (UK Offshore Operators Association - UKOOA) units within the UK North Sea graben. The data are based on a subset of released exploration and appraisal wells from within the UK North Sea graben areas. The well data are concentrated in the areas overlying the deep sedimentary basins of the Viking Graben, Central Graben and the Moray Firth Basin, with fewer wells over the adjacent platforms. The UKOOA lithostratigraphic classification has been applied consistently.
-
3D structured light surface scan of a fossil held within the BGS Type and Stratigraphical Reference Collection Sample number: BGS GSM 26215 Species: Lytoceras jurense (Ammonite) Age: Inferior Oolite Group, Jurassic Location: Quarry Hill, Chideock, Dorset
-
Clumped isotope analyses, raw data, replicates and temperatures calculated using the empirical calibration of Wacker et al. (2014), recalculated using the [Brand] isotopic parameters.
-

This dataset spans the Sinemurian-Pliensbachian boundary of the Llanbedr (Mochras Farm) drill core that was drilled onshore in the Cardigan Bay Basin, Wales, UK. This dataset contains 1. Micro-, macro-charcoal data and palynofacies, obtained at the University of Exeter (Streatham campus), UK, 2. Clay mineralogical data (X-ray diffraction (XRD)) obtained at the University of Burgundy, France, in collaboration with Jean-François Deconinck, 3. Carbon-isotope data, TOC and carbonate content, obtained at the University of Exeter (Penryn campus), UK. The dataset was created within the scope of the JET project (Integrated understanding of Early Jurassic Earth system and timescale) - https://gtr.ukri.org/projects?ref=NE%2FN018508%2F This project has received funding from the International Continental Scientific Drilling Programme (ICDP) and the UK Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). The PhD-project within this dataset was created is funded by the University of Exeter, UK.
-
Raw CT scan data for the following taxa (Euparkeria, Scelidosaurus, Lesothosaurus, Hypsilophodon, Herrerasaurus, Adeopapposaurus, Leyesaurus, Pantydraco, Heterodontosaurus, Coelphysis, Columba, Uromastyx), deposited as either .tif stacks or .dicom stacks, together with .vol files. CT reconstructions for each of these provided as .stls and in other file formats and also all files associated with the generation of Finite Element Models for each of these taxa. Reference photographs of specimens also provided where relevant. Scans and models are arranged in folders by taxon on a hard drive, accompanied by a Read Me file giving full details.
-

**Nothing Known About This**Grain size analysis and statistics of Jurassic-Cretaceous and Tertiary sands from East Dorset, the Hampshire Basin and Shaftesbury area. Analysis taken from selected sites therefore not complete cover of the area.
-
Terrestrial palaeo-environmental proxy data has been collected to examine orbital changes in wildfire activity in the Early Jurassic of the Mochras Borehole, Cardigan Bay Basin, Wales. To do this a high resolution charcoal abundance dataset was created and quantified in two size fractions, microscopic charcoal (10-125 µ) and macroscopic charcoal (>125 µ). To take potential changes in riverine influx and/or organic preservation in account on the charcoal abundance, palynofacies were analysed to document all terrestrial and marine organic particles present in the samples, and next to this, X-ray fluorescence data was gathered to assess detrital output. Mass spectrometry provided information on the carbonate and Total Organic Carbon content and bulk organic carbon isotopes. This information was used to look at changes in the lithology and the carbon cycle. Finally, clay mineralogical data was obtained to look at changes in the hydrological cycle in relation to wildfire activity. This dataset spans 951-934 mbs from the Mochras borehole, which is the time equivalent of ~350 kyr, in the Margaritatus Zone of the Upper Pliensbachian. The Mochras sediments have been deposited in the Cardigan Bay Basin, Wales. At the time of deposition, this location was positioned in the Laurasian Seaway at a paleolatitude of ~35°N. These datasets were obtained at a high resolution (10 cm) using X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, mass spectrometry and palynological preparations. This high resolution was acquired to analyse the presence of precessional orbital forcing on wildfire and the other proxy datasets. This data was collected, interpreted and analysed by Teuntje Hollaar, Claire Belcher, Stephen Hesselbo, Micha Ruhl, Jean-Franҫois Deconinck, Sarah Jane Baker and Luke Mander. The complete dataset presented in the published article file ‘Wildfire activity enhanced during phases of maximum orbital eccentricity and precessional forcing in the Early Jurassic’ has been included in this data file.
-
Registers of microfossil analyses carried out by FW Anderson in London mainly during the 1950s and 1960s, but includes older collections,notably those of Davis (1935) and Burrows (1948). Specimens recorded are mainly ostracods, but include some foraminifera and some charophytes and holothurians. Sample number, locality/borehole, specimen identifications, remarks, cross referencing to the SAM and other data sets are given. The set is arranged: MIK(M) 1-4483 in 41 volumes on Mesozoic (predominantly) ostracods MIK(T) 1-1590 in 11 volumes, Tertiary foraminifera MIK( C) 1-400 in 5 volumes, Carboniferous ostracods MIK (J) 1-1219 in 8 volumes Jurassic microfossils (few identifications) MIK(K) 1-677 in 7 volumes Cretaceous microfossils (identifications patchy) MIK(J)F, MIK(K)F and MIK(T)F are small foreign collections.
-

This dataset contains the collated wireline logs, stratigraphy and core analysis of the three boreholes drill as part of the publicly funded Rapid Global Geological Events Project (RGGE) which ran between 1995-1998. The aim of the RGGE project was to identify the effects of climatic changes on modern sediments. The project focused on the Kimmeridge Clay due to its unbroken sequence of fossiliferous marine mudstones. These mudstones have compositional variations in organic content, minerology, fauna and clay content which reflect changes in both the climate and sea level. Over the course of the project the entire sequence of the Kimmeridge Clay was cored across three boreholes, two at Swanworth Quarry and one at Metherhills.
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service