Aquifers
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
Resolution
-
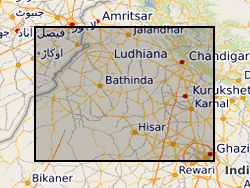
Thicknesses of aquifer units in the subsurface of the Indo-Gangetic foreland basin, northwestern India. Data are organised by borehole and indicate the thickness of aquifer units, separated by non-aquifer material.
-
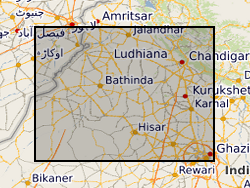
Matlab m-file code to generate a probabilistic model of aquifer-body occurrence in the subsurface of the Indo-Gangetic foreland basin, northwestern India. The accompanying ArcGIS ASCII matrix files give aquifer-body percentages in successive 10 m depth slices for use within the model. File xxx_01.txt is for depths 0-10 m, file xxx_02.txt for depths 10-20 m, etc.
-
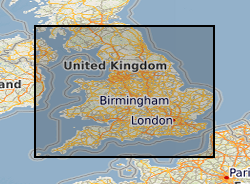
Joint BGS/Environment Agency dataset of aquifer designations for England and Wales at 1:50 000. The dataset identifies different types of aquifer - underground layers of water-bearing permeable rock or drift deposits from which groundwater can be extracted. These designations reflect the importance of aquifers in terms of groundwater as a resource (drinking water supply) but also their role in supporting surface water flows and wetland ecosystems. The maps are split into two different type of aquifer designation: superficial - permeable unconsolidated (loose) deposits (for example, sands and gravels), and bedrock - solid permeable formations e.g. sandstone, chalk and limestone.
-

This map layer shows the distribution of superficial deposits, as mapped at 1:250 000 scale, which are considered to have the potential to store and transmit significant amounts of groundwater. The areas defined are based upon a sub-set of superficial deposits as mapped by GSNI at 1:250 000 scale where the following mapped deposits are considered to have potentially significant permeability and storage properties: glacial sands and gravels, blown sand, raised beach deposits and alluvium. A regional, detailed assessment of the individual deposits in terms of their aquifer potential (aerial extent, thickness, saturated depth etc.) has not yet been undertaken. Hence formal classification of each deposit as an aquifer area is not possible at present. In some cases limited aerial extent or minimal thickness may result in the mapped geological deposit not being considered as an aquifer. Due to natural geological variability and data availability, this map cannot and is not intended to represent actual conditions on a site-specific scale. For site specific investigations more detailed geological and hydrogeological information is available from GSNI. Advice on groundwater management and protection matters is available from the GSNI hydrogeologist or by contacting the Groundwater Team at NIEA. Further information on the hydrogeology of Northern Ireland is available in Hydrogeology of Northern Ireland, Robins N S (1997) and Hydrogeological Map of Northern Ireland, BGS 1994 both of these are available from the BGS bookshop or from the GSNI office (note: the aquifer classification used on the 1994 hydrogeological published map differs from the classification shown on the GeoIndex layer). NOTE: When considering the distribution of aquifers within a certain area, reference should also be made to the bedrock aquifer layer, available on this website.
-

This vector contour dataset represents the calculated, estimated temperature distribution at 100 m depth. Method described in Busby, J., Lewis, M., Reeves, H. and Lawley, R., 2009, August. Initial geological considerations before installing ground source heat pump systems. Geological Society of London.
-

This dataset represents the thickness in metres of the Upper Devonian in the Midland Valley of Scotland (Stratheden Group and Kinnesswood Formation) over the extent of the model developed by Kearsey, T.I., Receveur, M. and Monaghan, A.A., 2024. Modelled hot sedimentary aquifer geothermal potential of Upper Devonian strata in the Midland Valley of Scotland. Uncertainties in the model are linked to the absence of boreholes penetrating both the top and the base of the Upper Devonian (except the Inch of Ferryton well) and poor seismic reflection data in the centre of the basin where it is thickest and deepest. The extent of the geological units is as shown on the published BGS geology maps, considering the re-interpretation of the Kinnesswood Formation as Devonian in age. The model is presented with high uncertainty.
-

This vector dataset represents the Variscan faults for the early Carboniferous limestone (ECL) in hot sedimentary aquifers in the UK, used by D J.R. Jones, T. Randles, T. Kearsey, T.C. Pharaoh, A. Newell (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2023.102649.
-

This vector contour dataset represents the calculated temperature distribution ( °C) at the base of the Permo-Triassic (PT) in the Cheshire and Worcester basins, considered for their hot sedimentary aquifer geothermal resource potential. The extent of the temperature maps corresponds to the extent of the modelled base PT in each basin. The maps and are based on temperature data from the latest revision of the UK Geothermal Catalogue (1987) compiled during the 1977-1991 Geothermal Energy Programme. For all basins taken together, the temperature ranges between 8.0 °C to 104.6 °C, with the highest temperatures found at depth in the Cheshire Basin. The dataset is used as a basis for the determination of the heat resource potential of the Permo-Triassic hot sedimentary aquifer resources (heat-in-place and heat recoverable). This dataset is derived from Rollin, K. E., G. A. Kirby, and W. J. Rowley. Atlas of geothermal resources in Europe: UK revision. British Geological Survey technical report WK/95/7, Regional Geophysics Group, 1995: https://webapps.bgs.ac.uk/data/publications/publication.html?id=21735106 and the European Geothermal Atlas (https://op.europa.eu/publication-detail/-/publication/9003d463-03ed-4b0e-87e8-61325a2d4456).
-

This vector dataset compiles the vertical and non-vertical faults for the top and base of the Sherwood Sandstone Group in the Permo-Triassic Worcester, Wessex, East Yorkshire Lincolnshire and Cheshire basins.
-

This vector contour dataset represents the calculated temperature distribution (°C) at the base of the Sherwood Sandstone Group (SSG) in the main Permo-Triassic Cheshire, Wessex and Worcester basins and the intra-SSG temperature in the East Yorkshire-Lincolnshire Basin, considered for their hot sedimentary aquifer geothermal resource potential. The extent of the temperature maps corresponds to the extent of the modelled base SSG in each basin. The maps and are based on temperature data from the latest revision of the UK Geothermal Catalogue (1987) compiled during the 1977-1991 Geothermal Energy Programme. For all basins taken together, the temperature ranges between 5.3 °C to 103.7 °C, with the highest temperatures found at depth in the Wessex Basin. The dataset is used as a basis for the determination of the heat resource potential of the Triassic hot sedimentary aquifers in the UK (heat-in-place and heat recoverable). This dataset is derived from Rollin, K. E., G. A. Kirby, and W. J. Rowley. Atlas of geothermal resources in Europe: UK revision. British Geological Survey technical report WK/95/7, Regional Geophysics Group, 1995: https://webapps.bgs.ac.uk/data/publications/publication.html?id=21735106 and the European Geothermal Atlas (https://op.europa.eu/publication-detail/-/publication/9003d463-03ed-4b0e-87e8-61325a2d4456).
 NERC Data Catalogue Service
NERC Data Catalogue Service